In This Blog
- What is Vitamin B1?
- Why Do We Need Vitamin B1?
- What Happens If You Don’t Get Enough Vitamin B1?
- Vitamin B1 Deficiency Symptoms
- Possible Causes of Vitamin B1 Deficiency
- Health Issues Caused by Prolonged Vitamin B1 Deficiency
- How Can You Consume Vitamin B1?
- Vitamin B1 Foods
- Vitamin B1 Dosage for Adults
- Vitamin B1 Dosage for Children
- Vitamin B1 Supplement
- Best Vitamin B1 Supplement
What is Vitamin B1?
Vitamin B1 is one of the water-soluble B vitamins. This essential B vitamin plays a vital role in forming red blood cells and other tissues in the human body. It is also used to help convert food into energy and to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
It plays a vital role in whole-body health and metabolism by facilitating the conversion of food into energy, supporting your body’s growth and development, improving mental function, maintaining healthy skin and eyes, supporting healthy immunity, and preventing fatigue by aiding in energy production. Vitamin B1 is found in many foods, including meat, poultry, fish, and certain fruits and vegetables.
Why Do We Need Vitamin B1?
Vitamin B1 assists in the body’s normal functioning. It helps the body to produce energy and maintain healthy skin, hair, and nails, as well as plays a role in many other body functions.
- Vitamin B1 is used in maintaining our nervous system functions. It also helps to maintain a healthy metabolism and cell growth.
- It is essential for healthy blood sugar levels because it aids in converting sugars into energy.
Highlights:
- Vitamin B1 plays a vital role in carbohydrate metabolism
- It helps you use glucose
- It’s involved in the synthesis of DNA and RNA
- It’s also a coenzyme that supports many essential reactions, such as carbohydrate metabolism required for energy production.
What Happens If You Don’t Get Enough Vitamin B1?
Vitamin B1 helps form red blood cells by helping them mature properly. This supports the transport of oxygen throughout your body. People with low vitamin B1 levels may have anemia or fatigue because their bodies do not have enough red blood cells to carry oxygen efficiently.
When we don’t get enough Vitamin B1, we may experience.
Possible Causes of Vitamin B1 Deficiency
Vitamin B1 deficiency can lead to adverse health issues. It goes without saying that Vitamin B1 is fundamental to normal body functioning and a healthy system. While Vitamin B1 Deficiency is not very common, lifestyle or habits can lead to vitamin deficiency. Some of the causes relating to Vitamin B1 deficiency can be:
- Poor diet or inadequate absorption from the intestines.
- Taking antacids containing aluminum hydroxide
- Taking excessive amounts of alcohol
- Drinking too much caffeine
- Having diarrhea for more than two days per week for at least three weeks
- Chewing large amounts of sugar-free gum
- Taking certain medications such as corticosteroids or antihistamines
- Having a medical condition that impairs your ability to absorb nutrients such as celiac disease or cystic fibrosis (CF).
- Eating foods that contain high amounts of vitamin C (such as oranges), which compete with thiamine for absorption.
Health Issues Caused by Prolonged Vitamin B1 Deficiency
Vitamin B1 deficiency is a health condition that can cause serious health problems. If we don’t get enough daily essential nutrients or constantly practice bad habits that lead to Vitamin B1 deficiency, it can result in (2) health conditions including:
- Anemia due to a lack of red blood cells or which can be caused by insufficient intake or impaired absorption of iron, folate, and vitamin B12
- Impaired mental function, such as memory loss and confusion.
- Heart issues, such as low blood pressure and a rapid heartbeat
- Vitamin B1 deficiency also can lead to nerve damage in your legs and feet (peripheral neuropathy).
How Can You Consume Vitamin B1?
Vitamin B1 is thiamine, which can be consumed through diet or health supplements. To ensure that you are getting an adequate amount of Vitamin B1 every day, you need to be conscious of what your daily diet looks like. Vitamin B1 can be obtained through food sources such as meat, poultry, fish, milk, and eggs. We will look at food rich in Vitamin B1.
Vitamin B1 Foods
- Beans – chickpeas, kidney beans, and lentils are good sources of vitamin B1.
- Spinach –contains a good amount of vitamin B1 and other vitamins such as vitamin C, E, and K. It also provides iron, calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus. Spinach has been found to reduce inflammation in the body by fighting free radicals that cause oxidative stress. Moreover, spinach is rich in antioxidants that (3) help fight cancer cells and boost immunity against viruses and bacteria.
- Yeast
- Grain products such as brown rice, whole wheat, and barley
- Cereals such as corn flakes, oatmeal, and bran flakes
- Peas and lentils
- Slices of bread such as white bread, whole grain bread, and rye bread (these foods contain a small amount)
- Potatoes (also known as potato chips) – are good sources of thiamine, but only if they are made from unrefined potatoes (organic potatoes generally contain more thiamine than non-organic ones). Eating canned or frozen potatoes won’t provide much thiamine because they have been cooked before being canned or frozen, making them less nutritious and more likely to contain chemicals that interfere with the absorption of thiamine by the body.
Vitamin B1 Dosage for Children
Children aged 4-13 years should take between 0.6- 0.9 mg per day; infants aged 0-3 months should take 0.3 mg per day while newborns should be given 0.2 mg per day.
Vitamin B1 Supplement
Eating nutritious foods is key to living a healthy life since it makes sure that you get all the essential vitamins and minerals you need every day. However, if you are not getting enough nutrients from foods, you may be at risk for developing anemia or low blood iron levels if you do not supplement with vitamin B1. When you know you’re not getting enough nutrients from daily meals, taking Vitamin B1 supplements may help you fill your nutritional gap.
Best Vitamin B1 Supplement
If you have a low energy level or noticed slower metabolism, you might want to supplement Vitamin B1 with health supplements. Although the Recommended Daily Intake (RDI) for Vitamin B1 is an average of 1.2mg for adults, drinking excessive alcohol or caffeine or poor gut health can affect the absorption of Vitamin B1 throughout the system.
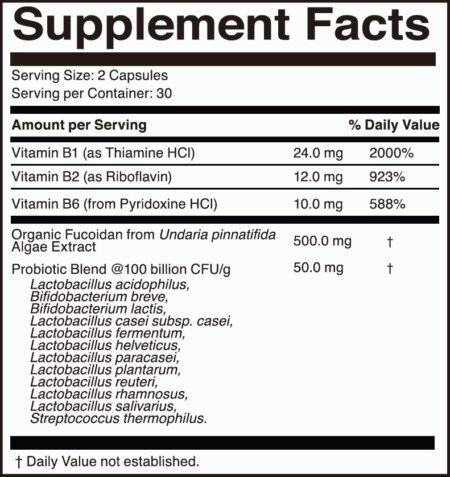
Brimmune Immune + Energy is an excellent choice to supplement Vitamin B1 with the RDI of Vitamin B1. Brimmune is formulated with daily essential vitamins B1, B2, and B6 to support cellular metabolism*, energy production*, and the immune system*.
Other key ingredients in Brimmune Immune + Energy, Fucoidan and Probiotics, will nourish your body and help support your immune system gut health*. Brimmune Immune + Energy incorporates 24mg of Vitamin B1 (as Thiamine HCI) per serving along with 500mg of certified organic Fucoidan, 50mg of Probiotics blend @ 100 billion CFU/g, 12mg of Vitamin B2 (as Riboflavin), and Vitamin B6 (as Pyridoxine HCI).
Taking a daily serving of Brimmune Immune + Energy will replenish your body with Vitamin B1 for your energetic and healthy lifestyle.
Key Takeaway
- Vitamin B1 is an essential vitamin for normal metabolism. It helps your body use carbohydrates and fats, convert food into energy, and store nutrients.
- Vitamin B1 plays a key role in making red blood cells, brain function, skin health, and bone health.
- Vitamin B1 deficiency is rare, but it can cause nerve damage and other neurological disorders, such as beriberi, which affects the heart and other organs.
- Vitamin b1 is water soluble: It passes through your system quickly. However, when consumed through meals, your body can only store a limited amount of Vitamin B1 in tissues and cells.
- Consider taking a Vitamin B1 supplement if you don’t get enough nutrients from food.